In the realm of fashion, children's attire often reflects the intersection of tradition and modernity. Among the various traditional styles that have made a comeback in recent years, Tang-style headwear stands out as a symbol of rich cultural heritage and fashionable allure. This article delves into the enchanting world of Tang-style headwear for children, exploring its historical roots, design elements, and the reasons behind its enduring popularity.
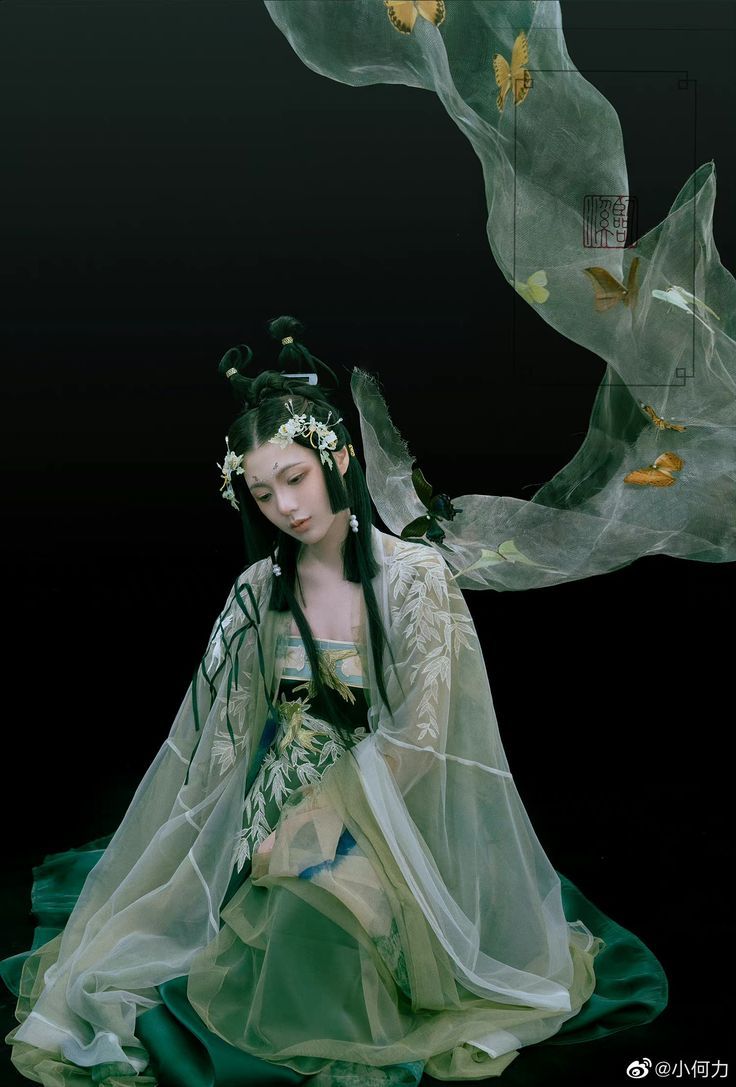

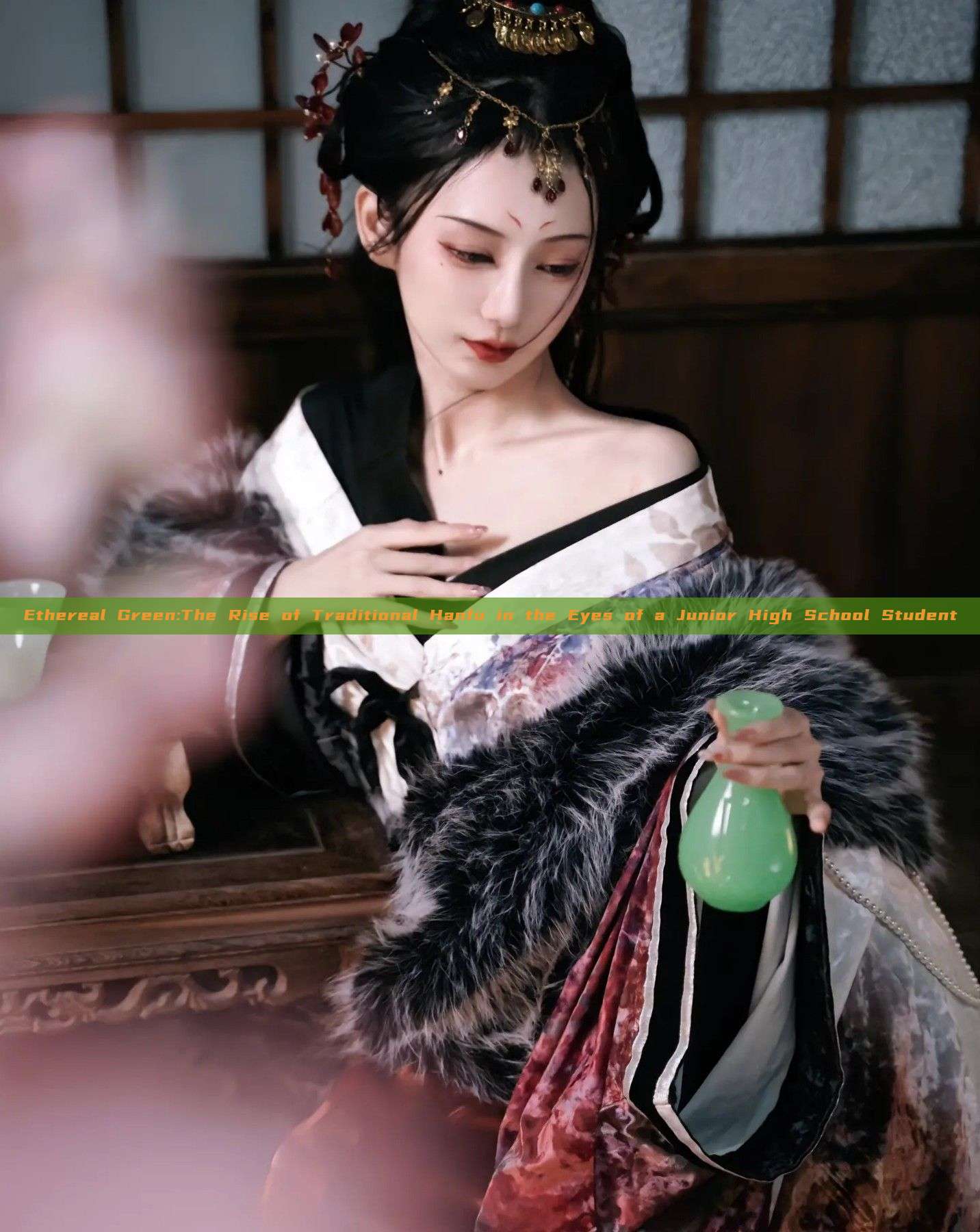
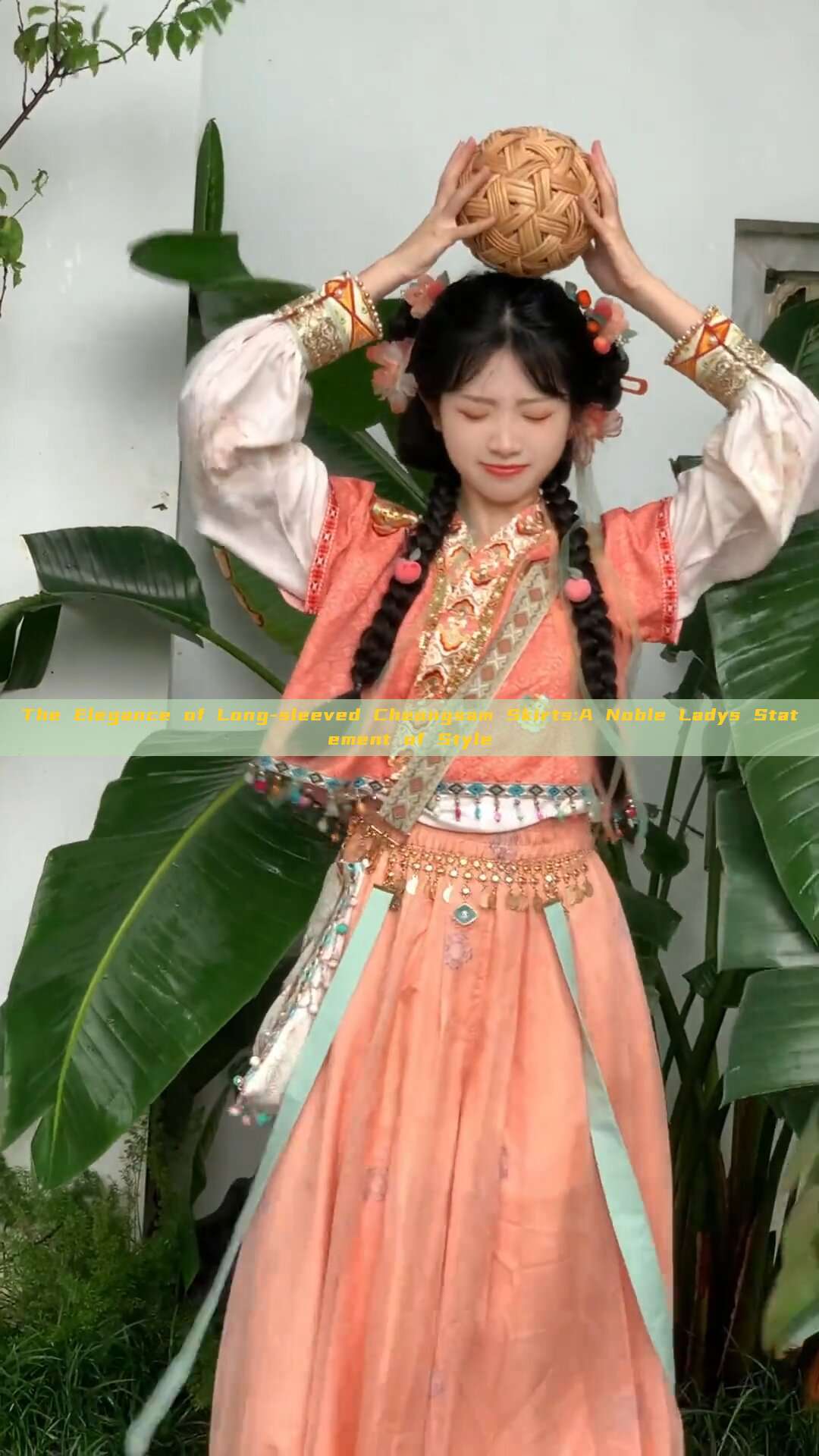
Tang-style headwear, originating from the Tang Dynasty in China, is a testament to the exquisite craftsmanship and intricate designs of ancient China. These headpieces are not just pieces of clothing; they are a gateway to a world of stories, legends, and cultural symbols. Children's Tang-style headwear, in particular, is a blend of traditional elements with contemporary designs, making it appealing to both parents and children.
The designs of Tang-style headwear for children are often vibrant and colorful, featuring intricate patterns and symbols that reflect the rich tapestry of Chinese culture. Common design elements include dragons, phoenixes, flowers, and auspicious symbols like the double happiness sign. These designs are often executed in vibrant colors like red, yellow, and gold, which not only make the headwear stand out but also evoke a sense of warmth and joy.
The materials used in the manufacture of these headpieces are equally important. Silk, cotton, and other natural fabrics are often used to create lightweight and comfortable headwear that children can wear without any discomfort. The use of traditional embroidery techniques like zhongshan embroidery further enhances the beauty and uniqueness of these headpieces.
The popularity of Tang-style headwear for children can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the headwear's unique design and vibrant colors make it stand out in a crowd. In today's world of fast fashion, where children often want to stand out from the rest, Tang-style headwear offers a unique and fashionable way to do so. Secondly, the headwear is often seen as a way to introduce children to their cultural heritage. As children become more aware of their cultural identity, wearing traditional headwear like Tang-style headwear becomes a way to celebrate their roots and heritage.
Moreover, Tang-style headwear is also seen as a way to promote traditional craftsmanship. As the world becomes increasingly focused on fast production and mass manufacturing, the art of traditional craftsmanship is often lost. By supporting the manufacture of Tang-style headwear, parents are not just buying a piece of clothing but also supporting a craft that has been passed down through generations.
However, it's important to note that while Tang-style headwear may be popular, it's not a necessary component of children's wardrobe. It should be seen as an option that parents can choose based on their child's preferences and their own values. The key is to strike a balance between respecting traditional culture and allowing children to express their individuality.
In conclusion, Tang-style headwear for children is not just a piece of clothing; it's a symbol of rich cultural heritage and contemporary fashion. It represents a blend of traditional craftsmanship and modern design, making it appealing to both parents and children. By supporting the manufacture of these headpieces, we are not just supporting a fashion trend but also preserving a craft that has been passed down through generations.
Moreover, Tang-style headwear offers an opportunity for parents to introduce their children to their cultural heritage and instill values of respect for traditional culture. By allowing children to wear these headpieces, parents are not just dressing their children in traditional attire; they are also teaching them about their cultural identity and the importance of preserving their rich cultural heritage. Ultimately, the popularity of Tang-style headwear for children is a testament to the enduring power of traditional culture and the importance of preserving it for future generations.